We had a lot of fight with our north Indian friend regarding our language. Its our diverse culture, and we should be proud of it. Here, we are going to find some interesting facts about Indian Languages!

Article 343(1) of the Constitution of India states that “The official language of the Union Government shall be Hindi in Devanagari Script”. “Unless Parliament decided otherwise the use of English for official purposes was to cease 15 years after the constitution came into effect”.That is on 26th January 1965.
It means over a period of 15 years since the commencement of the Indian Constitution,Hindi will replace English as the official language. However, Parliament can decide whether to use English as official language or not.
This led to a wide protest across the nation by the non Hindi speaking communities against the change in official language from English to Hindi.The protest resulted in the enactment of the official language act 1963.
This Act declares Hindi in Devanagari Script as the official language of the union. English has been given the status of “subsidiary official language” of the union.
The constitution of India made a provision for each of the Indian states to choose their own official language for communications at the state level.
There are many languages listed in the 8th schedule of the constitution which may be used by the States for official purpose. Initially 14 languages were selected under 8th schedule.
They were :
- Assamese
- Hindi
- Malayalam
- Punjabi
- Telugu
- Bengali
- Kannada
- Marathi
- Sanskrit
- Urdu
- Gujarati
- Kashmiri
- Odia
- Tamil
Later Sindhi was added as the 15th language through 21st Amendment Act of 1967.
Three languages were added by 71st Amendment Act 1992. They are Konkani, Manipuri and Nepali. 92nd Amendment Act 2003 added 4 more languages to the 8th schedule, they are Bodo,Mythili, Dogri and Santali.
At present there are 22 languages in total listed under the 8th schedule of Indian Constitution. India has no national language. Hindi is not a national language.Neither does the constitution nor any Act define the national language.
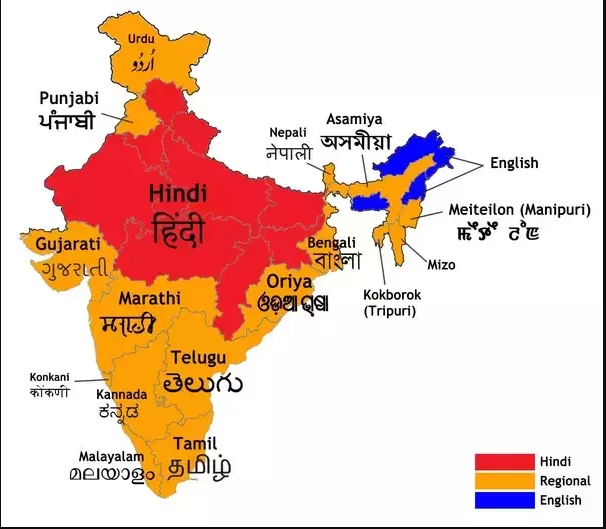
The Constitution does not specify the official language to be used by the states for the conduct of official functions. States are free to adopt it. The language to be adopted by the states need to be one of those listed in the 8th schedule, and several states have adopted official languages which are not in the list.
Examples:
- Tripura – kokborok
- Puducherry -French
- Mizoram -Mizo
English is the official language of Nagaland and Meghalaya.!!!But English is not in the list of 22 scheduled languages as per 8th schedule.










1 comment
Kuriappan Mathew
a good one (Y)